Introduction to Underactive Thyroid
The thyroid gland, a small butterfly-shaped organ located in the neck, plays a crucial role in regulating metabolism and energy levels. When this gland produces insufficient hormones, the condition is known as hypothyroidism or underactive thyroid. Recognizing the symptoms early can lead to timely intervention and management, improving the quality of life for those affected. This article delves into the various symptoms associated with an underactive thyroid, offering insights into how they manifest and impact daily life.
Common Symptoms of Hypothyroidism
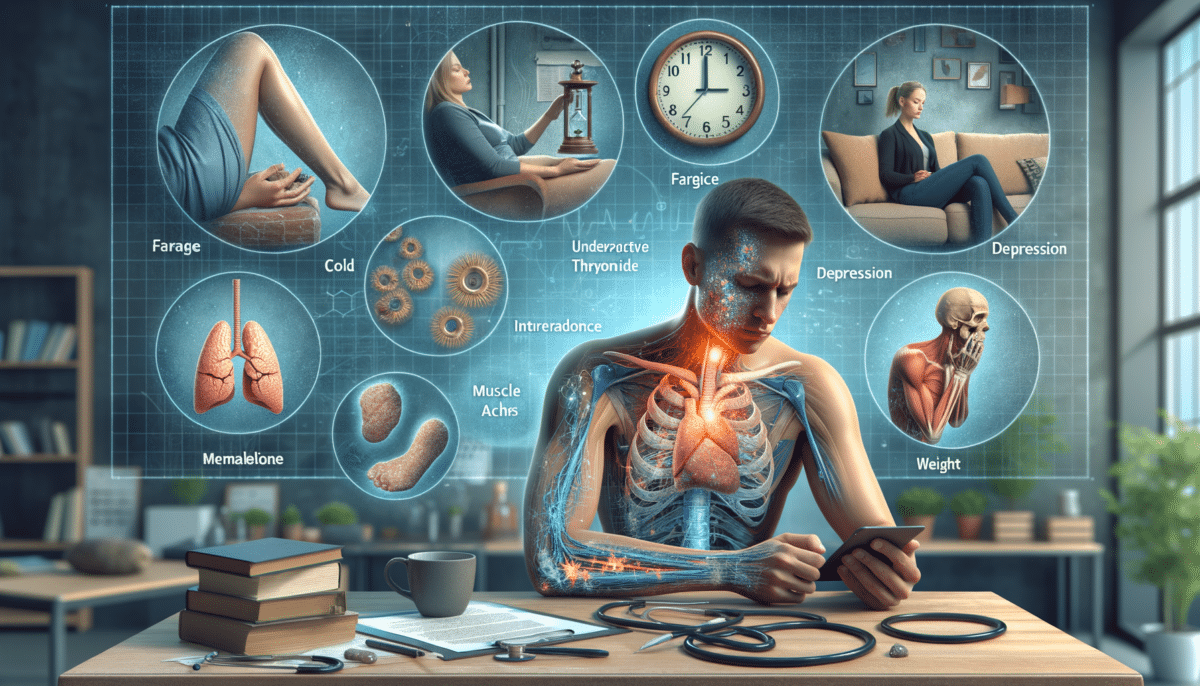
Hypothyroidism can present a variety of symptoms that often develop slowly over time. Some of the most common include:
- Fatigue: A persistent feeling of tiredness or lack of energy, even after adequate rest.
- Weight Gain: Unexplained weight gain or difficulty losing weight despite a healthy lifestyle.
- Cold Sensitivity: Increased sensitivity to cold temperatures, often feeling chilly when others are comfortable.
- Dry Skin and Hair: Skin may become dry and flaky, while hair may become brittle and fall out easily.
- Muscle Weakness: Generalized muscle weakness or cramps, especially in the arms and legs.
These symptoms can significantly affect daily activities and overall well-being, highlighting the importance of recognizing and addressing them promptly.
Impact on Mental Health
Beyond physical symptoms, an underactive thyroid can also impact mental health. Individuals may experience:
- Depression: A common symptom, often characterized by persistent sadness or a lack of interest in activities.
- Memory Problems: Difficulty concentrating or remembering information, commonly referred to as “brain fog.”
- Mood Swings: Unexplained changes in mood, which can affect personal and professional relationships.
These mental health symptoms can be particularly challenging, as they may be mistaken for standalone psychological issues. Understanding the link between hypothyroidism and mental health is crucial for comprehensive treatment.
Diagnosis and Testing
Diagnosing an underactive thyroid typically involves a combination of symptom evaluation and blood tests. The most common test measures the levels of Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) and thyroxine (T4) in the blood. Elevated TSH and low T4 levels usually indicate hypothyroidism. In some cases, additional tests may be required to determine the underlying cause of the thyroid dysfunction. Early diagnosis is key, as it allows for the initiation of treatment plans that can alleviate symptoms and prevent complications.
Managing Hypothyroidism
Management of an underactive thyroid primarily involves hormone replacement therapy, typically with synthetic thyroxine. This treatment aims to normalize hormone levels and alleviate symptoms. Regular monitoring and adjustments by healthcare providers are essential to ensure optimal dosing. Lifestyle modifications, such as a balanced diet rich in iodine and regular exercise, can also support thyroid health. Patient education and support are vital components of effective management, empowering individuals to take an active role in their health care.
Conclusion: Taking Charge of Thyroid Health
Understanding the symptoms of an underactive thyroid is the first step toward effective management and improved quality of life. By recognizing the physical and mental health impacts, individuals can seek timely medical advice and interventions. With proper treatment and lifestyle adjustments, those affected by hypothyroidism can lead fulfilling lives. Awareness and education remain critical in promoting early diagnosis and comprehensive care.