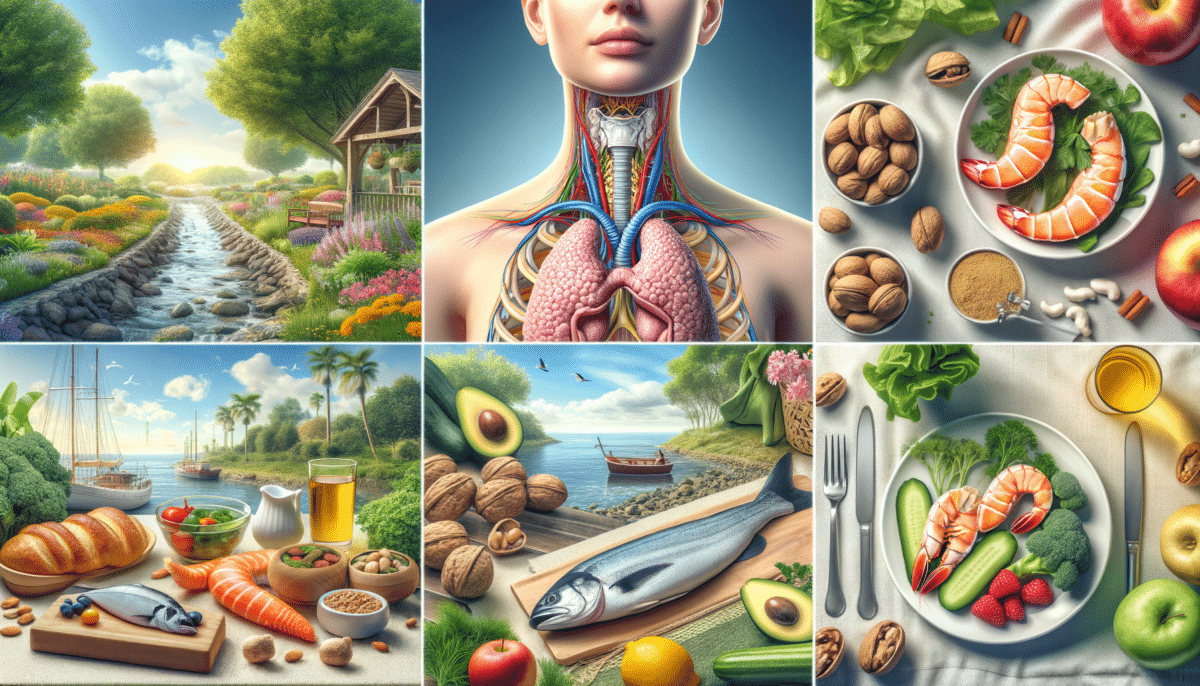
The Role of the Thyroid in the Body
The thyroid gland, a small butterfly-shaped organ located at the base of the neck, plays a pivotal role in regulating the body’s metabolism. It produces hormones such as thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which influence nearly every cell in the body. These hormones are essential for regulating metabolic rate, heart and digestive function, muscle control, brain development, and bone maintenance. The thyroid’s impact on metabolism means that any imbalance can lead to significant health issues. An underactive thyroid, or hypothyroidism, can result in fatigue, weight gain, and depression, while an overactive thyroid, or hyperthyroidism, can cause weight loss, increased heart rate, and anxiety. Understanding the thyroid’s role is the first step in recognizing the importance of maintaining its health.
Common Thyroid Disorders
Thyroid disorders are relatively common, affecting millions of people worldwide. The two primary types of thyroid disorders are hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism. Hypothyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland does not produce enough hormones, leading to symptoms such as fatigue, cold intolerance, and weight gain. On the other hand, hyperthyroidism is characterized by excessive hormone production, causing symptoms like rapid heartbeat, weight loss, and nervousness. Other thyroid conditions include thyroid nodules, which are lumps in the thyroid gland, and thyroid cancer. Autoimmune disorders such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and Graves’ disease are significant contributors to thyroid dysfunction. Early detection and treatment are crucial in managing these conditions effectively.
Impact of Diet on Thyroid Health
Diet plays a significant role in maintaining thyroid health. Certain nutrients are essential for optimal thyroid function, including iodine, selenium, and zinc. Iodine is crucial for hormone production, and a deficiency can lead to hypothyroidism. Foods rich in iodine include seafood, dairy products, and iodized salt. Selenium, found in Brazil nuts, fish, and eggs, helps convert T4 into the active T3 hormone. Zinc, present in meat, shellfish, and legumes, supports thyroid hormone synthesis. Conversely, excessive consumption of goitrogens, substances found in cruciferous vegetables like broccoli and cabbage, can interfere with thyroid hormone production. However, cooking these vegetables can reduce their goitrogenic effect. A balanced diet that includes these vital nutrients can support thyroid health and prevent disorders.
Lifestyle Habits Affecting Thyroid Function
Lifestyle choices can significantly impact thyroid health. Stress management is crucial, as chronic stress can lead to hormonal imbalances that affect the thyroid. Regular exercise helps maintain a healthy weight and supports metabolic function, both of which are vital for thyroid health. Additionally, smoking has been linked to an increased risk of Graves’ disease and other thyroid disorders, making smoking cessation an important step in maintaining thyroid health. Adequate sleep is also essential, as sleep deprivation can disrupt hormonal balance. By incorporating these healthy habits into daily life, individuals can support their thyroid function and overall well-being.
The Importance of Regular Thyroid Check-Ups
Regular thyroid check-ups are essential for early detection and management of thyroid disorders. Blood tests measuring levels of Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) and thyroid hormones T4 and T3 can provide insight into thyroid function. Early detection of thyroid imbalances allows for timely intervention, preventing complications and improving quality of life. People with a family history of thyroid disorders or those experiencing symptoms such as unexplained weight changes, fatigue, or mood swings should consider regular screenings. Consulting with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and treatment plans is crucial in managing thyroid health effectively.